Once a niche athletic supplement, branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) have exploded in popularity as a means to potentially improve muscle retention, endurance, and focus during workouts. (5) Now as synonymous with supplementation as the best protein powders and pre-workouts, the best BCAA supplements offer key benefits encased in flavorful profiles at affordable costs.
Given the landscape of the category, finding a proper BCAA powder or capsule for your training needs can be difficult at times. To lend a helping hand, we’ve called on our team of experts and diehard fitness enthusiasts to test over 20 BCAA supplements from top brands, examining each profile through the lens of our supplement testing methodology. We also consulted with Dr. Jennie Stanford, M.D. and Chelsea Rae Bourgeois, MS, RDN, LD to make sure we understood the purpose of BCAA supplements and how to best analyze them. Each BCAA supplement chosen for this round-up was rated in major areas relative to the category, including:
- Amino Acid Ratio: How are the BCAAs ratioed within the given formulation? Does the split across the leucine, isoleucine, and valine counts support effective performance?
- Listed Ingredients: Does the product contain BCAAs independently, or are there other additives to help fuel progress in other areas of training?
- Taste: Do the available flavors warrant continued use of the supplement? Is there enough variety to help defend against flavor fatigue?
- Solubility: How well do these products blend in a shaker bottle?
- Value: Does the listed cost per serving align with the results and effectiveness of the supplement, itself?
The BarBend team has helped connect over 1.6 million athletes with high-quality nutritional supplements to give them the boost they desire when it comes to health and wellness. If you’re searching for a new BCAA powder to add to your regular routine, we’re confident that the following details can help you shake up your supplementation (in a good way).
The 13 Best BCAA Supplements of 2025
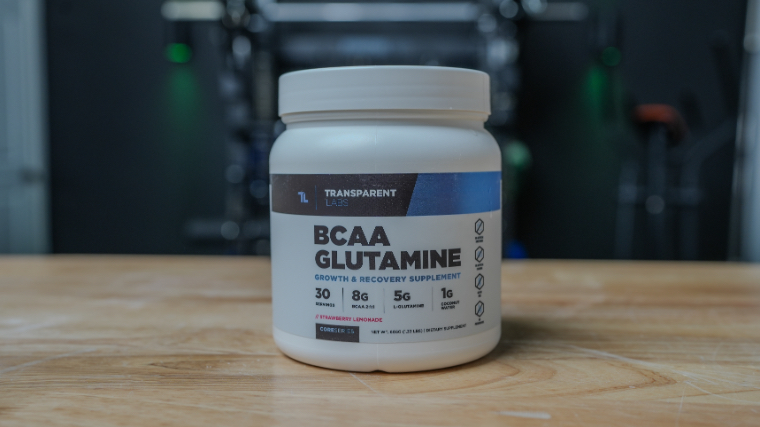
- Best BCAA Powder Overall: Transparent Labs BCAA Glutamine
- Best Budget BCAA: Nutricost BCAA
- Best BCAAs for Hydration: Snap Supplements BCAAs
- Best Unflavored BCAAs: Jacked Factory BCAA Powder
- Best BCAAs for Women: Promix BCAA Powder
- Best BCAAs Pills: Crazy Muscle BCAA Pills
- Best BCAA for Men: Transparent Labs Intra
- Best BCAAs for Muscle Growth: Momentous Vital Aminos
- Best Tasting BCAAs: Cellucor Alpha Amino
- Best Vegan BCAAs: Naked Nutrition Naked BCAAs
- Best BCAAs for Endurance Athletes: 1st Phorm BCAAs
- Best BCAAs for Recovery: MyProtein Essential BCAA 2:1:1
- Best BCAAs for Pre-Workout: EVLution Nutrition BCAA Lean Energy
Editor’s note: The content on BarBend is meant to be informative in nature, but it should not be taken as medical advice. The opinions and articles on this site are not intended for the diagnosis, prevention, and/or treatment of health problems. It’s always a good idea to talk to your doctor before beginning a new fitness, nutritional, and/or supplement routine.
Best BCAA Powder Overall: Transparent Labs BCAA Glutamine

This glutamine supplement is gluten-free, non-GMO, and free of artificial preservatives. Each container provides 30 servings that contain 5000 milligrams of l-glutamine and 1,535 milligrams of vitamin C.
Specs
- BCAAs: 8g at 2:1:1 ratio
- Key Ingredients: Glutamine, coconut water powder, vitamin C
- Flavors: Sour Green Apple, Tropical Punch, Strawberry Lemonade, Unflavored, Blue Raspberry
- Dosage: 1 scoop
- Sweeteners: Stevia
- Price Per Serving: $1.33
Read our full Transparent Labs BCAA Glutamine Review.
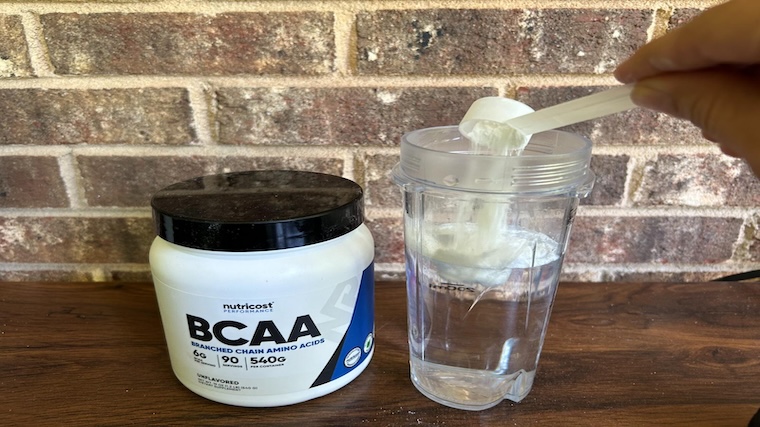
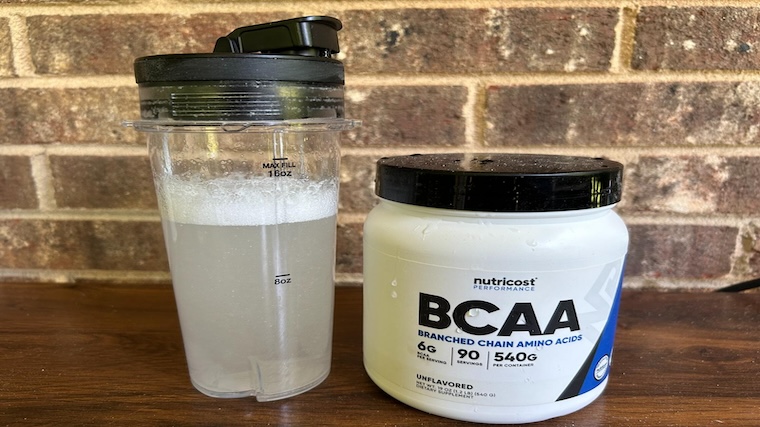
Best Budget BCAA: Nutricost BCAA

This Nutricost offering delivers a high-quality 2:1:1 ratio of BCAAs in an unflavored formulation that can be easily added to your pre-workout or other beverage of choice. Plus, this BCAA powder is gluten-free, non-GMO, an vegetarian friendly making it a solid selection for those with strict dietary needs.
Specs
- BCAAs: 6g at 2:1:1 ratio
- Key Ingredients: Just BCAAs
- Flavors: Unflavored, Grape, Pineapple, Raspberry Lemonade, Strawberry Kiwi, Watermelon, Green Apple, Orange Mango, Peach Pear
- Dosage: 1 scoop
- Sweeteners: Sucralose
- Price Per Serving: Starting at $0.25
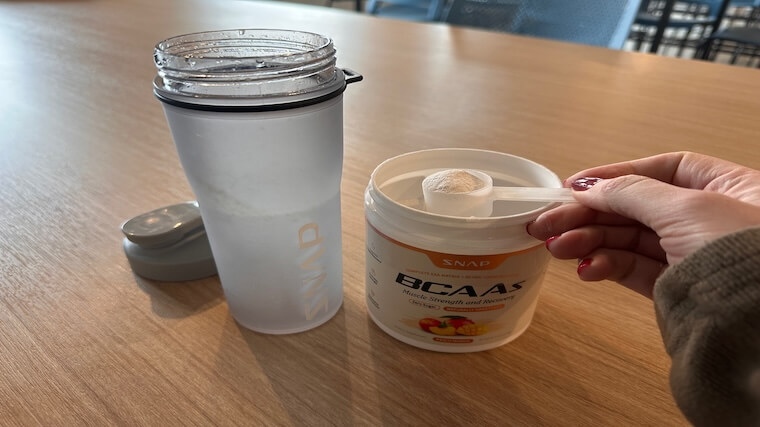
Best BCAAs for Hydration: Snap Supplements BCAAs

This plant-based BCAA powder from Snap Supplements includes 5 g of BCAAs, an essential amino acid blend, a nitric oxide booster blend, and a hydration and antioxidant blend. Available in two flavors, you can save by signing up for a subscription.
Specs
- BCAAs: 5g at 2:1:1 ratio
- Key Ingredients: Sodium, potassium, plant-based BCAAs, essential amino acids (EAAs), l-citrulline, l-arginine, l-taurine, coconut water powder, pomegranate berry extract
- Flavors: Pomegranate Watermelon, Peach Mango
- Dosage: 1 scoop (approximately 9.2 grams)
- Sweeteners: Organic stevia
- Price Per Serving: $1.10
Best Unflavored BCAAs: Jacked Factory BCAA Powder

This product contains a blend of 3,000mg of leucine, 1,500mg of isoleucine, and 1,500mg of valine. It comes in three flavors — Blue Raspberry, Fruit Punch, and Unflavored, all of which are created using both natural and artificial flavorings.
Specs
- BCAAs: 6g
- Key Ingredients: Just BCAAs
- Flavors: Unflavored, Blue Raspberry, Fruit Punch
- Dosage: 1 scoop
- Sweeteners: Not listed
- Price Per Serving: $0.67
Best BCAA for Women: Promix BCAA Powder

Promix BCAAs come in five different flavors and they include 100 percent of your daily vitamin C value.
Specs
- BCAAs: 5g
- Key Ingredients: Ingredients vary by chosen flavor
- Flavors: Raspberry Lemon, Mixed Berry, Cherry Lime, Strawberry Lemon, Unflavored
- Dosage: 2 scoops
- Sweeteners: Monk fruit
- Price Per Serving: $1.07
Best BCAAs Pills: Crazy Muscle BCAA Pills

Crazy Muscle BCAA Pills offer a standard 2:1:1 ratio of amino acids to help bolster muscle growth, energy stores during training, and recovery time. These capsules can also be ideal for those wanting extra convenience across their supplement regimen with a single serving consisting of just three pills.
Specs
- BCAAs: 3g at 2:1:1 ratio
- Key Ingredients: Just BCAAs
- Flavors: None
- Dosage: 3 capsules
- Sweeteners: None listed
- Price Per Serving: $0.25
Best BCAA for Men: Transparent Labs Intra

Transparent Labs Intra Workout EAA not only contains the three BCAAs, but it also contains the six additional EAAs. This product includes 6.7 grams of EAAs, as well as 2 grams of citrulline malate and 1 gram of ElevATP.
Specs
- BCAAs: 3.81g at 2:1:1 ratio
- Key Ingredients: EAAs, taurine, BetaPure betaine anhydrous, l-tyrosine, coconut water powder, elevATP, AstraGin
- Flavors: Strawberry Lemonade, Blue Raspberry
- Dosage: 1 scoop
- Sweeteners: Stevia
- Price Per Serving: $1.50
Best BCAAs for Muscle Growth: Momentous Vital Aminos

This supplement blends nine essential amino acids to help build strength and improve your performance. One bag costs $44.95 and comes in a tropical punch flavor.
Specs
- BCAAs: 3.75g
- Key Ingredients: Just BCAAs
- Flavors: Tropical Punch
- Dosage: 1 scoop
- Sweeteners: None listed
- Price Per Serving: $1.53
Best Tasting BCAAs: Cellucor Alpha Amino

With zero grams of sugar, this is an ideal formula for anyone on the low-carb, high-fat keto diet. It also packs 750mg of creatine HCL for improved in-gym performance.
Specs
- BCAAs: 5g at 2:1:1 ratio
- Key Ingredients: Phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, potassium, instantized BCAAs, EAAs, BetaPower betaine anhydrous, coconut water powder, dipotassium phosphate, disodium phosphate, dimagnesium phosphate
- Flavors: Fruit Punch, Icy Blue Razz, Watermelon
- Dosage: 1 scoop
- Sweeteners: Sucralose
- Price Per Serving: $0.93
Read our full Cellucor Alpha Amino Review.
Best Vegan BCAAs: Naked Nutrition Naked BCAAs

This product is certified vegan, gluten-free and clean of any artificial ingredients. The BCAAs come in a 2:1:1 ratio, and the cost is just $0.35 per serving.
Specs
- BCAAs: 5g at 2:1:1 ratio
- Key Ingredients: Ingredients vary by chosen flavor
- Flavors: Unflavored, Strawberry Lemonade, Cherry Lime
- Dosage: 1 scoop
- Sweeteners: Fermented cane sugar (flavored profiles only)
- Price Per Serving: Starting at $0.35
Best BCAAs for Endurance Athletes: 1st Phorm BCAAs

This BCAA supplement offers the ideal 2:1:1 ratio of BCAAs as well as an added dose of electrolytes. Plus, our testers loved the taste.
Specs
- BCAAs: 7.5g
- Key Ingredients: Niacin, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, sodium, potassium, BCAAs, amino blend, potassium citrate, sodium chloride, TRAACS magnesium bisglycinate chelate, potassium glycinate complex
- Flavors: Berry Lemonade, Blue Raspberry, Green Apple, Lemonade, Pineapple Mango, Strawberry Candy
- Dosage: 1 scoop
- Sweeteners: Sucralose
- Price Per Serving: $1.12
Best BCAAs for Recovery: MyProtein Essential BCAA 2:1:1

A well-priced BCAA that's super easy to consume on the go.
Specs
- BCAAs: 4g
- Key Ingredients: Ingredients vary by chosen flavor
- Flavors: Blue Raspberry, Peach Rings, Rainbow Sherbet, Snow Cone, Unflavored, Watermelon
- Dosage: 3 scoops
- Sweeteners: Sucralose
- Price Per Serving: Starting at $0.73
Best BCAAs for Pre-Workout: EVLution Nutrition BCAA Lean Energy

This energetic powder combines 5 grams of BCAAs with 110 milligrams of “natural energizers” to help support your pre- and post-workout needs. The four available flavors, while definitely sweet, can also be a nice treat that has you returning to your container day in and day out.
Specs
- BCAAs: 5g
- Key Ingredients: Ingredients vary by chosen flavor
- Flavors: Furious Grape, Cherry Limeade, Fruit Punch, Blue Raz
- Dosage: 2 scoops
- Sweeteners: Sucralose
- Price Per Serving: Starting at $0.83
How We Tested and Chose the Best BCAAs
The BarBend team is composed of competitive athletes, certified personal trainers, nutrition coaches, and lifelong fitness enthusiasts. To determine the best BCAA supplements available today, we tested 26 different products from high-quality brands, using our supplement testing methodology as guidance in rating each silhouette in a range of categories. Ratings were scored on a scale of 1 (lowest) to 5 (highest) in categories such as the following:
- Amino Acid Ratio: We prioritize products with a 2:1:1 ratio of BCAAs. The standard formulation for these products is 2 or 3 grams of leucine for every gram of isoleucine and valine.Products with lower ratios may not be as effective.
- Third-Party Testing: We favor products with third-party testing from independent labs. Third-party testing verifies label accuracy so you know the ingredients on the label match what’s actually in the container.
- Ergogenic Effects: Alongside BCAAs, many products include ergogenic aids or ingredients linked to enhanced exercise performance. These can include citrulline, beta-alanine, and caffeine. We included picks on this list that incorporate these additional ingredients, as well as products that don’t.
- Taste: Although taste is subjective, we assign a rating based on whether a product is true to its flavor name. We share our thoughts on the sweetness, aftertaste, and bitterness of various products.
- Solubility: We favor products that dissolve easily without clumping or leftover floaties.
Benefits of BCAAs
BCAAs are the building blocks of protein, and when you consume complete protein sources like chicken, beef, fish, or whey protein powder, you are consuming BCAAs. If your diet is rich in high-quality protein sources, chances are you’re already getting the benefits of BCAAs. BCAA supplements aren’t a must-have but they may support muscle growth and improve athletic performance. Here are a few benefits you may see with consistent BCAA use:
- Improved Muscle Mass: Leucine, one of the three BCAAs, plays a role in stimulating muscle protein synthesis, which is needed to build muscle. (17) The recommended “threshold” for leucine intake is often noted as two to three grams per day for maximized muscle building potential. (17)
- Improved Performance: BCAA supplementation may be able to help improve your performance by preventing fatigue while you train. (3)(6)
- Improved Reaction Time: Although more firm research is needed, BCAA supplements may be able to help improve your reaction time during athletic performance. (7)
Potential Negatives of BCAAs
Studies report that regular BCAA consumption has shown to cause no adverse effects. (23) However, taking BCAAs featuring other ingredients like artificial sweeteners or known allergens can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, bloating, and other unwanted symptoms. For BCAAs containing caffeine and other stimulants, Dr. Raj Dasgupta, MD states, “Athletes with known sensitivities to the effects of caffeine may experience side effects such as anxiety, insomnia, or headaches, even with lower doses below the FDA’s 400-milligram daily recommendation.” (24)
There’s also concerns over BCAAs and their relationship to insulin resistance. “The relationship between BCAAs and insulin resistance is complex, as BCAAs cause the liver, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscles to have different metabolic responses,” says Dr. Jennie Sanford, MD. “BCAAs do not cause systemic insulin resistance, but when they are metabolized poorly, this can be a sign of underlying insulin resistance that needs to be addressed.”
As with every supplement — from the best multivitamins to proteins, pre-workouts, and beyond — it’s always advisable to take your personal sensitivities into question prior to purchase. You can also speak to your personal healthcare provider if you’re looking for more detailed information on which ingredients and dosages align with your personal needs and wants.
How Much Do BCAAs Cost?
BCAAs can be a fairly expensive individual supplement, typically ranging in price from $20 to $50. It’s best to look at the price per serving to truly know how much bang you’re getting for your buck. You’ll likely find that BCAAs go for anywhere between $0.20 and $3.00 per serving. On average, BCAA supplements cost about $0.90 per serving.
| Best BCAA Powder Overall | Transparent Labs BCAA Glutamine | $1.33 |
| Best Budget BCAA | Nutricost BCAA | Starting at $0.25 |
| Best BCAAs for Hydration | Snap Supplements BCAAs | $1.10 |
| Best Unflavored BCAAs | Jacked Factory BCAA Powder | $0.67 |
| Best BCAA for Women | Promix BCAA Powder | $1.07 |
| Best BCAAs Pills | Crazy Muscle BCAA Pills | $0.25 |
| Best BCAA for Men | Transparent Labs Intra | $1.50 |
| Best BCAAs for Muscle Growth | Momentous Vital Aminos | $1.53 |
| Best Tasting BCAAs | Cellucor Alpha Amino | $0.93 |
| Best Vegan BCAAs | Naked Nutrition Naked BCAAs | Starting at $0.35 |
| Best BCAAs for Endurance Athletes | 1st Phorm BCAAs | $1.12 |
| Best BCAAs for Recovery | MyProtein Essential BCAA 2:1:1 | Starting at $0.73 |
| Best BCAAs for Pre-Workout | EVLution Nutrition BCAA Lean Energy | Starting at $0.83 |
What to Consider Before Buying BCAAs
“For people who regularly eat animal proteins, your diet probably includes sufficient amounts of BCAAs,” notes Dr. Jennie Stanford, MD. “However, amino acids are needed for a number of physiologic functions, and when you don’t have enough circulating amino acids, your body will break down muscle tissue to release them. So, for extended periods without consuming protein or even working out in a fasting state, BCAAs can help maintain lean muscle mass.”
Before purchasing a BCAA supplement, you may want to consider a few important factors. As BCAA supplements can vary substantially, you’ll want to consider ingredients, dosages, formulation, price, and the necessity of BCAAs before making a decision. We detail each of these more below.
Ingredient List
The ingredient lists on BCAA supplements can vary drastically from one supplement to another. You’ll want to consider what you’re looking for in a BCAA supplement and what you hope the outcome of taking one will be. If you’re looking strictly for BCAAs, you may want to opt for a simple formulation with a minimalist ingredient list. If you’re looking for BCAAs to be a part of your supplement regimen, but not the entirety of it, you may want to choose one with a solid dose of BCAAs as well as other ingredients, like glutamine, citrulline, or electrolytes.

For those looking to combine BCAAs with electrolytes, Dr. Raj Dasgupta, MD has an important note to consider. “It’s important to remember that sodium is the most abundant electrolyte lost in sweat, so if you’re looking for a supplement with added electrolytes to fuel your extensive training in intense conditions, be sure to confirm that sodium replenishment is feasibly achievable with the formulation of choice.”
Dosages
You’ll also want to consider how many grams of BCAAs each product offers.The recommended breakdown for BCAAs is a 2:1:1 ratio of leucine to isoleucine to valine for best potential effect. (18) Many supplements on the market have 4 grams in total of BCAAs, but you will find some supplements on this list that contain up to 8 grams as well. Some prefer to opt for a higher amount of BCAAs for effectiveness or potential recovery benefits.
Formulation
Are you looking for straight BCAAs or do you want something more robust? More complex formulations will often include BCAAs with several other ingredients that offer exercise enhancing benefits. BCAAs are also commonly found in pre-workout supplements and are naturally occurring in the best protein powders. Some people prefer to take straight BCAAs as an additional supplement in their stack.Others prefer to include them wrapped up in another supplement, which can cut down on the number of supplements they’re taking.

You’ll also want to consider whether you want a flavored powder, unflavored powder, or a pill formulation. Some people enjoy the taste of sweet, tangy, or fruity supplements, while others prefer pills for a convenient on-the-go supplement for the gym or while traveling. There is no wrong answer, just the answer that best suits your lifestyle.
Price
Many supplements can be really helpful additions to your supplement lineup and may help you achieve your goals more efficiently, but they shouldn’t empty your bank account. Your budget will be a major consideration when you’re picking out your perfect BCAA supplement. That’s why we provided options for every budget.
What are Amino Acids?
In the simplest of terms, amino acids are molecules that form proteins within the body. In total, there are 20 amino acids, and nine of which are labeled as “essential” meaning the body cannot produce them internally, so they must be consumed through the diet.
Debating between BCAAs versus EAAs comes down to the molecular structure of the amino acids themselves, since BCAAs are EAAs, in theory. The distinguishing factor, as the name suggests, is the branched-chain structure of the molecules that make up leucine, isoleucine, and valine — the three BCAAs. The remaining EAAs include histidine, methionine, threonine, lysine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan.
What’s In Your BCAAs?
We know that supplement labels can involve a lot of jargon and be tough to understand for the average person. Let’s break down what you’re most likely to see on your ingredients label, starting with the three branched-chain amino acids.
- Leucine: Leucine has the closest link with boosting muscle protein synthesis, as it activates this process. While your total calories are essential for muscle growth and muscle retention, muscle protein synthesis is a vital part of the puzzle. (8)
- Isoleucine: Used in the biosynthesis of proteins, this branched-chain amino acid plays a role in muscle metabolism, as it may help prevent muscle breakdown and promote fat burning. (9)
- Valine: This has some links to endurance and focus. Interestingly, if you have difficulty digesting it, and it accumulates in the blood, this could indicate insulin resistance, a risk factor for diabetes and other conditions. (10) (11)
- Glutamine: Glutamine may help reduce delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS) following a workout. (12) It also has some links to muscle gain, but most research has only seen this among people whose bodies are in physical trauma — it hasn’t translated to gains for gym-goers. (12)
- Beta Alanine: Found in pre-workouts, one-and-a-half to four grams has been shown to improve endurance and possibly aid in muscle hypertrophy. It’s possible that it also has some anti-aging effects, as it can increase the amount of carnosine (an antioxidant) in the body. (13)
- Citrulline Malate: Citrulline is a nitric oxide booster, which can lead to better circulation and blood flow. In workouts, this can translate to better endurance and power output. It’s also a common ingredient in erectile dysfunction supplements. (14)
- L-Carnitine plus L-Tartrate: These are linked to longevity, as they may improve mitochondrial function, and they could also help retain lean muscle mass and enhance aerobic output. (15)
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C may reduce cell damage from free radicals that occur during exercise. It’s a powerful antioxidant, which can be helpful for immune support. (16)
- B Vitamins: The eight B vitamins play a role in energy metabolism, the process that converts protein, carbs, and fat into energy. They may also help with brain function and cell health. (2)
- B Vitamins: The eight B vitamins play a role in energy metabolism, the process that converts protein, carbs, and fat into energy. They may also help with brain function and cell health. (2)
BCAA Supplements FAQs
What are BCAAs?
It stands for branched-chain amino acid. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein and the branched chain amino acids are those most closely associated with muscle protein synthesis, the process by which protein is produced to repair and retain muscle.
Do I need to take BCAAs?
Probably not, so long as you’re eating plenty of protein and calories throughout your day. If that’s the case, taking extra BCAAs around a workout probably won’t serve much extra benefit. Where BCAAs appear to have the most use is when the athlete is exercising on an empty stomach, isn’t eating much quality protein with a meal, or wants to retain their muscle during a fast or during a long period without protein. If you fall into those categories, BCAAs may be useful.
What is the best BCAA supplement?
While there are a wide variety of BCAA supplements that are great, our favorite is Transparent Labs BCAA Glutamine. It contains 8,000mg of BCAAs and we like the addition of vitamin C.
When should I take BCAAs?
It’s best to take BCAAs before or during your workout, depending on which kind you are using. A few BCAA supplements will say that you can take them before, during, or after a workout, but as far as basic BCAA supplements go, they’re probably most effective if you take them pre-workout. (2) For anyone who’s going hard at the gym, intra-workout BCAAs may be helpful in warding off fatigue. (3)
Can I take BCAAs without working out?
In theory, yes, you can consume BCAAs without working out as their benefits related to endurance, muscle retention, and workout recovery aren’t solely tied to physical fitness. That said, if you’re already consuming enough BCAAs through your whole-food diet, you may not need to supplement with these powders and capsules.
References
- Steenbergen, L., Sellaro, R., Hommel, B., & Colzato, L. S. (2015). Tyrosine promotes cognitive flexibility: evidence from proactive vs. reactive control during task switching performance. Neuropsychologia, 69, 50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.01.022
- Kennedy D. O. (2016). B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy–A Review. Nutrients, 8(2), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8020068
- AbuMoh’d, M. F., Matalqah, L., & Al-Abdulla, Z. (2020). Effects of Oral Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) Intake on Muscular and Central Fatigue During an Incremental Exercise. Journal of human kinetics, 72, 69–78. https://doi.org/10.2478/hukin-2019-0099
- Kaspy, M. S., Hannaian, S. J., Bell, Z. W., & Churchward-Venne, T. A. (2023). The effects of branched-chain amino acids on muscle protein synthesis, muscle protein breakdown and associated molecular signaling responses in humans: an update. Nutrition research reviews, 1–14. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954422423000197
- Salem, A., Trabelsi, K., Jahrami, H., AlRasheed, M. M., Boukhris, O., Puce, L., Bragazzi, N. L., Ammar, A., Glenn, J. M., & Chtourou, H. (2024). Branched-Chain Amino Acids Supplementation and Post-Exercise Recovery: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Journal of the American Nutrition Association, 43(4), 384–396. https://doi.org/10.1080/27697061.2023.2297899
- Kim, D. H., Kim, S. H., Jeong, W. S., & Lee, H. Y. (2013). Effect of BCAA intake during endurance exercises on fatigue substances, muscle damage substances, and energy metabolism substances. Journal of exercise nutrition & biochemistry, 17(4), 169–180. https://doi.org/10.5717/jenb.2013.17.4.169
- Wiśnik, P., Chmura, J., Ziemba, A. W., Mikulski, T., & Nazar, K. (2011). The effect of branched chain amino acids on psychomotor performance during treadmill exercise of changing intensity simulating a soccer game. Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme, 36(6), 856–862. https://doi.org/10.1139/h11-110
- Holwerda, A. M., Paulussen, K. J. M., Overkamp, M., Goessens, J. P. B., Kramer, I. F., Wodzig, W. K. W. H., Verdijk, L. B., de Groot, L. C. P. G. M., & van Loon, L. J. C. (2019). Leucine coingestion augments the muscle protein synthetic response to the ingestion of 15 g of protein following resistance exercise in older men. American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism, 317(3), E473–E482. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00073.2019
- Trautman, M. E., Green, C. L., MacArthur, M. R., Chaiyakul, K., Alam, Y. H., Yeh, C. Y., Babygirija, R., James, I., Gilpin, M., Zelenovskiy, E., Green, M., Marshall, R. N., Sonsalla, M. M., Flores, V., Simcox, J. A., Ong, I. M., Malecki, K. C., Jang, C., & Lamming, D. W. (2024). Dietary isoleucine content defines the metabolic and molecular response to a Western diet. bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology, 2025.05.30.596340. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.05.30.596340
- Tsuda, Y., Yamaguchi, M., Noma, T., Okaya, E., & Itoh, H. (2019). Combined Effect of Arginine, Valine, and Serine on Exercise-Induced Fatigue in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study. Nutrients, 11(4), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040862
- Bloomgarden Z. (2018). Diabetes and branched-chain amino acids: What is the link?. Journal of diabetes, 10(5), 350–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-0407.12645
- Legault, Z., Bagnall, N., & Kimmerly, D. S. (2015). The Influence of Oral L-Glutamine Supplementation on Muscle Strength Recovery and Soreness Following Unilateral Knee Extension Eccentric Exercise. International journal of sport nutrition and exercise metabolism, 25(5), 417–426. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2014-0209
- Gasmi, A., Mujawdiya, P. K., Lysiuk, R., Shanaida, M., Peana, M., Piscopo, S., Beley, N., Dzyha, S., Smetanina, K., Shanaida, V., Résimont, S., & Bjørklund, G. (2024). The Possible Roles of β-alanine and L-carnosine in Anti-aging. Current medicinal chemistry, 10.2174/0109298673263561231117054447. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.2174/0109298673263561231117054447 .
- Pérez-Guisado, J., & Jakeman, P. M. (2010). Citrulline malate enhances athletic anaerobic performance and relieves muscle soreness. Journal of strength and conditioning research, 24(5), 1215–1222. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181cb28e0
- Fielding, R., Riede, L., Lugo, J. P., & Bellamine, A. (2018). l-Carnitine Supplementation in Recovery after Exercise. Nutrients, 10(3), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030349
- Carr, A. C., & Maggini, S. (2017). Vitamin C and Immune Function. Nutrients, 9(11), 1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111211
- Plotkin, D. L., Delcastillo, K., Van Every, D. W., Tipton, K. D., Aragon, A. A., & Schoenfeld, B. J. (2021). Isolated Leucine and Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation for Enhancing Muscular Strength and Hypertrophy: A Narrative Review. International journal of sport nutrition and exercise metabolism, 31(3), 292–301. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2020-0356
- Khemtong, C., Kuo, C. H., Chen, C. Y., Jaime, S. J., & Condello, G. (2021). Does Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) Supplementation Attenuate Muscle Damage Markers and Soreness after Resistance Exercise in Trained Males? A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients, 13(6), 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061880
- Ferrando, A. A., Wolfe, R. R., Hirsch, K. R., Church, D. D., Kviatkovsky, S. A., Roberts, M. D., Stout, J. R., Gonzalez, D. E., Sowinski, R. J., Kreider, R. B., Kerksick, C. M., Burd, N. A., Pasiakos, S. M., Ormsbee, M. J., Arent, S. M., Arciero, P. J., Campbell, B. I., VanDusseldorp, T. A., Jager, R., Willoughby, D. S., … Antonio, J. (2023). International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Effects of essential amino acid supplementation on exercise and performance. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 20(1), 2263409. https://doi.org/10.1080/15502783.2023.2263409
- Armstrong L. E. (2021). Rehydration during Endurance Exercise: Challenges, Research, Options, Methods. Nutrients, 13(3), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030887
- Smith, J. W., Krings, B. M., Peterson, T. J., Rountree, J. A., Zak, R. B., & McAllister, M. J. (2017). Ingestion of an Amino Acid Electrolyte Beverage during Resistance Exercise Does Not Impact Fluid Shifts into Muscle or Performance. Sports (Basel, Switzerland), 5(2), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports5020036
- Ra, S. G., Miyazaki, T., Kojima, R., Komine, S., Ishikura, K., Kawanaka, K., Honda, A., Matsuzaki, Y., & Ohmori, H. (2018). Effect of BCAA supplement timing on exercise-induced muscle soreness and damage: a pilot placebo-controlled double-blind study. The Journal of sports medicine and physical fitness, 58(11), 1582–1591. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0022-4707.17.07638-1
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Nutrition, Trauma, and the Brain, Erdman J, Oria M, & Pillsbury L. (1970, January 1). Branched-chain amino acids. Nutrition and Traumatic Brain Injury: Improving Acute and Subacute Health Outcomes in Military Personnel. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK209312/
- Commissioner, O. of the. (2024, August 28). Spilling the beans: How much caffeine is too much?. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/spilling-beans-how-much-caffeine-too-much