These are two super popular whey proteins that are both very different, both in the kinds of protein they contain and the fact that one of them contains way, way more ingredients than the other.
Which one you’ll choose won’t just hinge on which one is cheaper, or tastier. (Though those qualities are easy to figure out.) They have vastly different ingredients, macronutrients, micronutrients, and digestion rates.
Dymatize’s Iso 100 is probably the most popular whey hydrolysate-based protein powder on Earth. BSN’s Syntha-6 isn’t quite as widespread but it has an unusual approach to protein blends that produces a mixture of several kinds of whey, casein, and even some egg white.
So which is best for your needs? Let’s break it down.

A protein powder comprised mostly of hydrolyzed whey, which may help you recover more quickly than other forms of whey.

This protein is great for an all-around snack with 22 grams of protein, 15 grams of carbs, and 6 grams of fat. The long ingredients list can be a pro or con depending on if you're a protein purest, or someone looking to cover a lot of needs in one shake.
How We Decide the Best
We don’t just go by what tastes better — there are a lot of ways to weigh whey.
Types of Protein
There are three kinds of whey, each with their own pros and cons: concentrate is cheapest, but has the most lactose and fat; hydrolysate absorbs the most quickly but it’s the most expensive. Then there’s casein, egg, milk protein isolate, and plenty of others.
Protein Per Calorie
If you want as much protein and as little fat and carbs as possible, it’s worth looking at how much protein you’re getting per calorie. Pure protein is 4 calories per gram. If you’re getting 20 calories per gram of protein, there’s a lot more fat and carbs. Close to 4 is ideal for some people, depending on their goals.
Sweeteners
Sucralose, acesulfame potassium, stevia, aspartame, different folks have different aversions here but we make sure to point out what’s being used just in case you have issues.
Additives
Soy, sunflower, corn, sugar, enzymes, gums… depending on your preferences, you may have something to say about these ingredients.
Note that we’re not making value judgments. None of these qualities are inherently good or bad. Soy probably isn’t evil, artificial sweeteners probably aren’t bad for you, but you’re well within your rights to minimize or avoid them in your diet so we’re just pointing out these and other potentially problematic ingredients.
Taste
Hey, we’re not going to ignore the importance of taste, here. Creamy, sweet, bland, powdery, you need to know to make the right choice.
Price
People generally buy protein powders for their protein, so it doesn’t make a lot of sense to compare them by cost per serving if one product has a bigger scoop. We use cents per gram of protein to make the best judgement.
The Companies
Dymatize
Based in Dallas, Texas, Dymatize was launched more than 20 years ago and their best known protein is easily Iso 100, which their managing director has called their flagship product.
An interesting fact is that all of Dymatize’s products are tested by Informed Choice, a third party testing site that ensures there are no banned substances in the finished product. This could be particularly good news for competitive athletes.
[Read our full Dymatize Iso 100 review!]
BSN
Founded in 2001, BSN stands for Bio-Engineered Supplements and Nutrition and ships to over 40,000 retailers in the United States. It’s pretty darn popular, due in no small part to the fact that their products are very reasonably priced.
But it’s also because they offer such a wide variety of products to suit different consumer needs, including no less than seven different protein powders. Syntha-6 is their best known.
[Don’t miss the full BSN Syntha-6 review!]
Nutrition
Dymatize
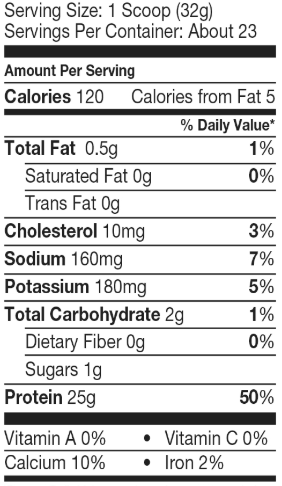
One scoop is 120 calories: 25 grams of protein, 2 grams of carbs (no fiber, 1 gram of sugar), and 0.5 grams of fat (none saturated). That’s 4.8 calories per gram of protein.
There’s not a lot else to talk about here, all the other nutrients are pretty low besides 10 percent of your calcium RDI. There’s also 3 percent of your cholesterol, 7 percent of your sodium, and 2 percent of your iron.
BSN
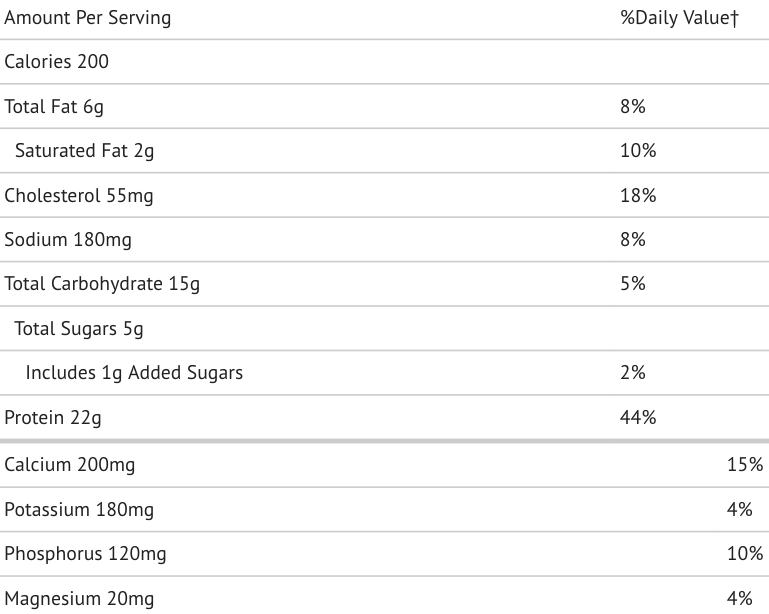
One scoop is quite a bit larger than Dymatize (47 grams versus 32 grams) but it still has less protein per serving: one scoop is 200 calories with 22 grams of protein, 15 grams of carbs (5 grams fiber, 2 grams sugar), and 6 grams of fat (2 grams saturated). That’s 9.1 calories per gram of protein.
Otherwise there’s 23 percent of your daily cholesterol, 9 percent of your sodium and potassium, and 8 percent of your iron.
So BSN has a lot more fiber and vitamins and minerals, but way more fat, cholesterol, and carbs.
[Curious about how Dymatize stacks up to lower carb whey proteins? Check out our comparison of Dymatize vs Isopure!]
Ingredients
Dymatize
Dymatize is mostly hydrolyzed whey. It also contains whey isolate, but it’s best known as a hydrolyzed whey based protein powder.
That’s the most processed form of whey. The most basic form is concentrate, then there’s isolate (which has a lot of the carbs and lactose and fat stripped out), then you’ve got hydrolysate, which is further broken down with enzymes or acid to the point where it’s sort of considered partially digested. That means it digests more quickly.(1)
Now for a lot of folks there’s not really a practical difference there, but the fact that it digests faster has been seen in some studies have suggested that it can speed recovery. One published in the Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport in 2010 found that athletes who were working out twice a day recovered their more power quickly with hydrolysate than a group taking whey isolate.(2) Now, you’re probably not an elite athlete working out twice a day. But some people still prefer hydrolyzed whey.
The rest of the ingredients list is short: natural and artificial flavors, salt, soy lecithin, potassium chloride, and the artificial sweetener sucralose.
BSN
BSN has pretty much every protein except hydrolyzed whey. There’s a “protein matrix” of whey concentrate, whey isolate, calcium caseinate, micellar casein, milk protein isolate, egg albumin, and some glutamine peptides.
So what does all that do? Basically, it means that it provides a mixture of fast and moderate and slow digesting proteins. This is marketed as an “anytime” protein, so what that means is it will continue to release amino acids into the bloodstream over time (3) There are a lot of companies that say this means it’s better for muscle protein synthesis, as in it will trigger that response for a longer period of time. Some rodent studies have indeed found that a combination of whey and casein is better for long term muscle protein synthesis if that’s your goal, but again, the practical difference for the average athlete is probably small.(4)
[For more information on muscle protein synthesis, check out our video on soy and strength athletes!]
The rest of the ingredients are numerous. Sunflower powder (sunfloiwer oil, corn syrup solids, sodium caseinate, mono- and di-glycerides, dipotassium phosphate, tricalcium phosphate, tricalcium phosphate, soy lecithin, and tocopherols), polydextrose, natural & artificial flavors, MCT powder (medium chain triglycerides, non-fat dry milk, disodium phosphate, silicon dioxide), lecithin, salt, cellulose gum, acesulfame potassium, sucralose, papain, and bromelain.
So that’s a lot of ingredients and there are more that people might take issue with: two kinds of artificial sweeteners (sucralose and acesulfame potassium), there’s corn, there’s gum.
To be fair, most people aren’t really bothered by these and one potential advantage is the digestive enymes papain and bromelain, which some studies have suggested might help with bloating and indigestion.(5)(6)
Taste
Dymatize
Both of these products have achieved the rare feat of being tasty with water. I’ve tried the Gourmet Chocolate and Chocolate Peanut Butter flavors of Iso 100 and they’re both tasty, though very sweet. If you don’t have much of a sweet tooth, you may prefer Syntha-6.
BSN
I’ve tried the Chocolate Milkshake and Banana Cream flavors and look, more carbs and more fat means usually means more flavor. That’s the case with Syntha-6. Perhaps because of the sunflower creamer, MCT fats, and the dried milk, Syntha-6 tastes way creamier than Iso 100 and if someone handed it to me pre mixed, I might believe it had been mixed with milk instead of water.
So if you like sweet, go with Dymatize. If you prefer creamy, go with BSN.
Price
Dymatize
The standard tub of Iso-100 is just 1.6 pounds and the price varies enormously, from 29 to 56 dollars. Usually you’ll find it for closer to $35, which makes it about $1.50 per scoop or 6-ish cents per gram of protein.
BSN
The 2.9-pound tub is between $28 and $33, so it’s between $1 and $1.20 per scoop or, on average, just under 5 cents per gram.
Both of these decrease in cost the more you buy, but since hydrolyzed whey is more expensive to produce, it’s not a big surprise that it’s the costlier of the two.
The Verdict
Dymatize Pros
- May be better for fast recovery
- More protein per calorie
- Way lower in cholesterol
- Less likely to trigger lactose sensitivities (<0.5 grams of lactose per scoop)
BSN Pros
- Better for long-term muscle protein synthesis
- Better for any time
- Cheaper
- More vitamins and minerals and fiber
- Contains digestive enzymes
These are pretty different products and the difference comes down to individual preference. It’s hard to argue that Iso 100 is more strictly a protein powder: it has way more protein per calorie. Syntha-6 is cheaper and may be easier on the stomach, provided you don’t have lactose issues. Both can be great sources of protein depending on your goals.
References
1. Potier M, et al. Comparison of digestibility and quality of intact proteins with their respective hydrolysates. J AOAC Int. 2008 Jul-Aug;91(4):1002-5.
2. Buckley JD, et al. Supplementation with a whey protein hydrolysate enhances recovery of muscle force-generating capacity following eccentric exercise. J Sci Med Sport. 2010 Jan;13(1):178-81.
3. Boirie Y, et al. Slow and fast dietary proteins differently modulate postprandial protein accretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Dec 23;94(26):14930-5.
4. Kanda A, et al. Effects of Whey, Caseinate, or Milk Protein Ingestion on Muscle Protein Synthesis after Exercise. Nutrients. 2016 Jun 3;8(6).
5. Muss C, et al. Papaya preparation (Caricol®) in digestive disorders. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2013;34(1):38-46.
6. Zhou Z, et al. Inhibition of Epithelial TNF-α Receptors by Purified Fruit Bromelain Ameliorates Intestinal Inflammation and Barrier Dysfunction in Colitis. Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 10;8:1468.