There are two types of protein in milk: whey and casein. Both can aid in muscle growth and recovery after a workout, but many prefer casein protein powder because it digests slower and is typically more filling than whey. Its slow-digesting nature is why it’s been deemed the best pre-sleep protein option: It feeds your muscles an extended-release dose of amino acids while you snooze. (1)(2)
Given the popularity of protein powders and the potential advantages of casein, how do you decide which is the best product on the market? Our team of BarBend experts tested more than 100 of the best protein powders to gather first-hand experience—and had registered dietitians analyze the formulas for popular products—to build a list of the best casein protein powders. Whether you’re after the best-tasting casein, the best all-natural casein, or simply the best budget casein, we have a pick for you.
The 7 Best Casein Protein Powders of 2025
- Best Casein Protein: Transparent Labs Casein
- Best Tasting Casein Protein: Legion Casein+
- Best Casein Protein for Digestion: Naked Nutrition Casein
- Best Natural Casein Protein: Muscle Feast Grass Fed Micellar Casein
- Best Budget Casein Protein: Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard Casein
- Best Casein Protein for Baking and Pudding: Dymatize Elite Casein
- Best Casein Protein for Athletes: Ascent Native Fuel Micellar Casein
Medical disclaimer: The content on BarBend is meant to be informative in nature, but it should not be taken as medical advice. The opinions and articles on this site are not intended to diagnose, prevent, and/or treat health problems. It’s always a good idea to talk to your doctor before beginning a new fitness, nutritional, and/or supplement routine. Individual needs for vitamins and minerals will vary.
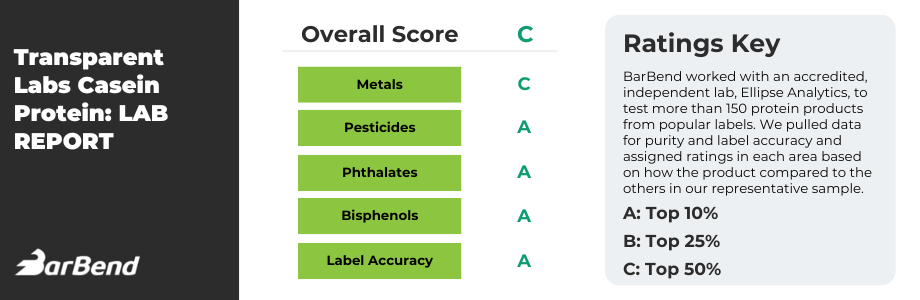
Best Casein Protein Overall: Transparent Labs Casein Protein

Free of artificial flavors, colors, and sweeteners, Transparent Labs Grass-Fed Casein is an incredibly straightforward supplement without fillers. It's also remarkably low in fat and carbohydrates.
Specs
- Protein: 25g
- Flavors: Chocolate
- Sweeteners Used: Stevia extract
- Third-Party Testing: Informed Choice Certified and Informed Protein Certified
- Price per Serving: $1.99
Read our full Transparent Labs Casein Protein Review.
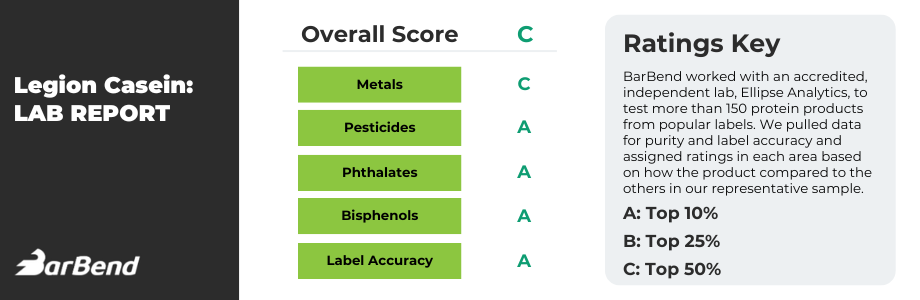
Best Tasting Casein Protein: Legion Casein+

Legion's Casein+ has more protein per calorie than any other casein we've seen, plus it has no artificial ingredients. Each serving provides 5.2 grams of branch chain amino acids.
Specs
- Protein: 25g
- Flavors: Dutch Chocolate, Cinnamon Cereal, French Vanilla, Strawberry
- Sweeteners Used: Stevia extract
- Third-Party Testing: Lab Tested for Purity
- Price per Serving: $2
Best Casein Protein for Digestion: Naked Nutrition Casein

Naked Nutrition's Micellar Casein Protein Powder has no artificial flavors, sweeteners, or colors and 26 grams of protein per serving. We also like that this formula has zero additives.
Specs
- Protein: 26g
- Flavors: Unflavored, Chocolate, Vanilla
- Sweeteners Used: Organic coconut sugar
- Third-Party Testing: Yes
- Price per Serving: $1.05
Best Natural Casein Protein: Muscle Feast Grass-Fed Micellar Casein

This inexpensive casein is all-natural and sourced from grass-fed cows. It is available either flavored or unflavored in a two or four-pound tub.
Specs
- Protein: 19g
- Flavors: Unflavored, Chocolate
- Sweeteners Used: Stevia
- Third-Party Testing: N/A
- Price per Serving: $1.28
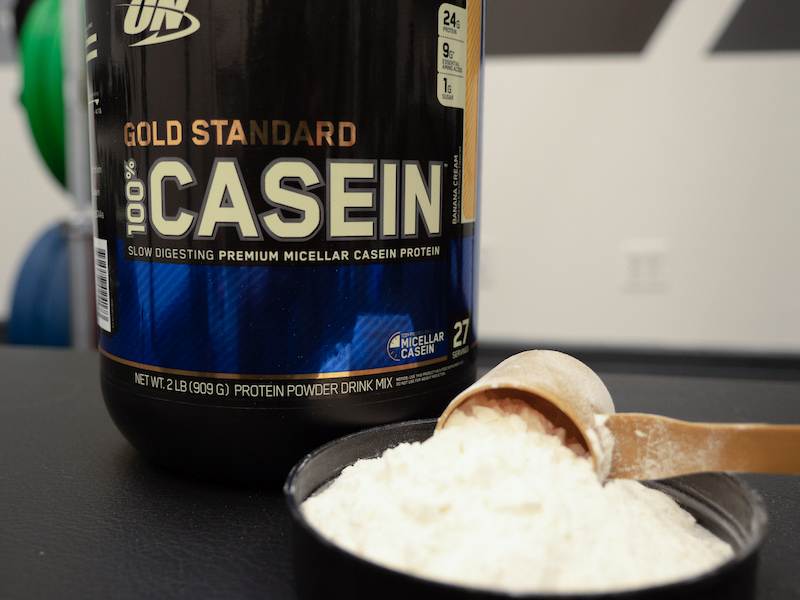
Best Budget Casein Protein: Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard Casein

Well-rounded, well-priced casein that contains enzymes that might improve its digestion. Each single-scoop serving packs 24 grams of protein and just a single gram of sugar.
Specs
- Protein: 24g
- Flavors: Chocolate Peanut Butter, Chocolate Supreme, Cookies & Cream, Vanilla
- Sweeteners Used: Sucralose
- Third-Party Testing: N/A
- Price per Serving: $1.52
Read our full Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard Casein Review.
Best Casein Protein for Baking and Pudding: Dymatize Elite Casein

This casein mixes well and has an unusual, low-fat creamer that makes for a great flavor. Each single-scoop serving provides 25 grams of protein and is sugar-free.
Specs
- Protein: 25g
- Flavors: Chocolate, Chocolate and Peanut Butter, Chocolate and Whey Protein Powder, Cinnamon Bun, Cookies & Cream, Vanilla
- Sweeteners Used: Sucralose
- Third-Party Testing: Informed Choice Certified
- Price per Serving: $1.33
[Related: Dymatize Iso 100 Protein Powder Review — Is Hydrolyzed Best?]
Best Casein Protein for Athletes: Ascent Native Fuel Micellar Casein

This slow-digesting protein powder is all-natural, soy-free, and tested for banned substances by Informed Sport. It's available in three different flavors in either a 32 or 64-ounce pounch.
Specs
- Protein: 25g
- Flavors: Chocolate, Chocolate Peanut Butter, Vanilla
- Sweeteners Used: Monk fruit extract
- Third-Party Testing: Informed Sport Certified
- Price per Serving: $1.70
Read our full Ascent Native Fuel Micellar Casein Review.
How We Tested and Chose the Best Casein Proteins
Our team of BarBend experts, including personal trainers, certified nutrition coaches, and athletes, tested more than 100 different protein products to help narrow down all the best casein proteins. As we sampled different options, these are the factors we considered using our supplement testing methodology.
- Formula: We looked at the amount of protein per serving relative to carbohydrates and fat. We opted for casein products that contained mostly protein with few other macros. We also prioritized products that had as few added ingredients, such as sweeteners and dyes, as possible.
- Flavors: We know that flavor is a pretty subjective factor, so we tried to prioritize options with multiple taste options. Our testers also tried to sample as wide a variety of flavors as possible.
- Solubility: In some cases, a shaker cup may not help the product sufficiently dissolve. Not everyone wants to pull out the blender to make a protein shake, so we made sure that each of the options on this list dissolved well using just a blender ball.
- Third-Party Testing: As often as possible, we like to prioritize products that have been third-party tested. That helps ensure that the products are free of banned substances and actually contain the contents written on the label.
[Related: Best Whey Protein Powders]
Benefits of Casein Protein
As most gym-goers know, protein is an extremely important macronutrient for building muscle mass and making strength gains. It’s also important for muscle recovery. (15) It is one of three macronutrients, and it’s one of your greatest tools when it comes to hitting your gym goals. So why choose casein?
- Supplement protein needs: For many people, it can be difficult to consume the amount of daily protein needed to assist muscle repair and growth, so a supplement like casein can be of great benefit for adding in an easy 20 grams (or more) of protein.
- Complete protein: Casein comes from cow’s milk, which makes it a complete protein that contains all nine essential amino acids, including the ever-important BCAAs (leucine, isoleucine, and valine). (16)
- Slower-digesting: Many people opt for a casein protein over other types because it may have better potential benefits when taken right before bed, which some people prefer over traditional use right after a workout. One study suggested that when casein is ingested right before bed, it may have the ability to increase muscle protein synthesis during sleep for better muscle mass and strength gains. (2)
- Adds variety: Utilizing a casein supplement may also make hitting your protein goals a little more interesting and enjoyable. If you’re tired of chicken breasts and eggs, casein may be a fun alternative to get an easy 20 or more grams of protein in a quick snack. Casein can be made into a delicious pudding consistency, or when frozen, an ice cream texture, which makes it a macro-friendly dessert or treat you won’t soon tire of.
How Much Does Casein Protein Cost?
Casein protein can cost anywhere from about $1.40 per serving up to $2.50 per serving. The cost per tub varies depending on how many servings are in the tub, among other factors.
| Best Casein Protein | Transparent Labs Casein | $1.99/serving |
| Best Tasting Casein Protein | Legion Casein+ | $2/serving |
| Best Casein Protein for Digestion | Naked Nutrition Casein | $1.05/serving |
| Best Natural Casein Protein | Muscle Feast Grass-Fed Micellar Casein | $1.28/serving |
| Best Budget Casein Protein | Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard Casein | $1.52/serving |
| Best Casein Protein for Baking and Pudding | Dymatize Elite Casein | $1.33/serving |
| Best Casein Protein for Athletes | Ascent Native Fuel Micellar Casein | $1.70/serving |
What To Consider Before Buying Casein Protein
Whether this is a new supplement in your routine or you’ve been taking it for a while, there are a few things worth thinking about before making the purchase.
Casein Type
Many companies act like it’s a huge deal that they only use micellar casein — the kind that’s encased in a globular structure called a micelle. But the vast majority of casein powders use micellar casein; this isn’t unusual. Calcium caseinate and hydrolyzed casein are less common and more processed, so micellar casein is typically the way to go.
Formula
Take a gander at the macronutrient ratio and make sure the protein powder you’re interested in is really a protein powder—that is, it doesn’t contain excess carbs and/or fats when what you want is protein. Look for a maximum of 3 grams of fat and 6 grams of carbohydrates.
Also look at the ingredients list to ensure it doesn’t contain anything you don’t want to consume, such as artificial sweeteners, artificial flavors, or preservatives. (13)(17)
Solubility
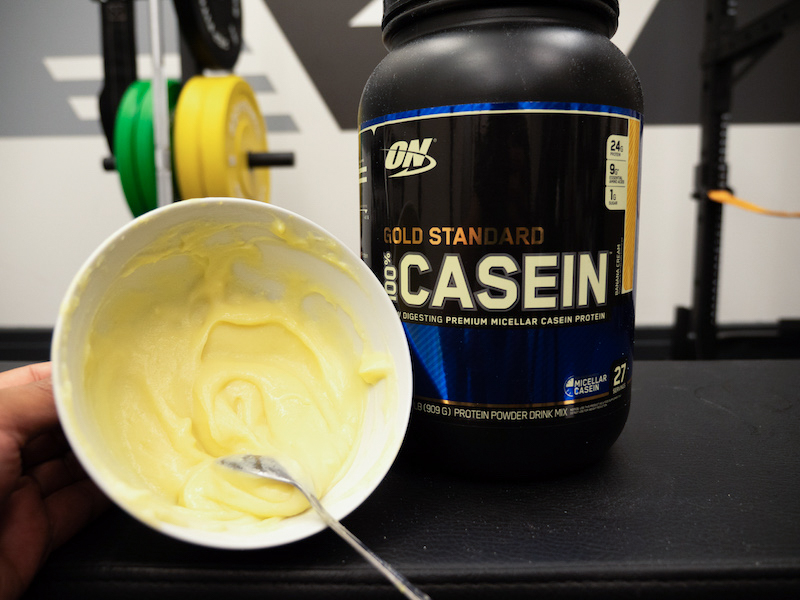
This is a huge advantage that casein has over whey. If you add water or (even tastier) milk to casein in a 3:2 ratio and stir it up for a few minutes, it becomes a pudding-like substance. Eat it straight away or freeze it for a few hours, and it becomes ice cream (which you can then blend up with additional liquid to make a milkshake—yum). If you plan on making either pudding or ice cream with your casein powder, make sure you select a preferable flavor for doing so.
However, this consistency may not be ideal for every athlete. Instead, some may prefer a standard shake. So, before you buy, consider your purposes for the supplement.
Flavor
If you’re going to be consuming a casein protein relatively frequently, you want a flavor that you actually enjoy. So, read product reviews carefully to settle on a taste that you won’t get sick of. Also, if you plan to bake with your casein, we recommend opting for a flavor that’s versatile, like chocolate or vanilla.
[Related: Does The Ketogenic Diet Work For Strength Training?]
Whey vs. Casein: Is One Better?
Both whey and casein are sourced from milk (they get separated in the cheesemaking process), and they’re both really high quality proteins (meaning they contain all your essential amino acids). But the question remains: Is one superior to the other?
By and large, research tells us no. In one commonly cited study, police officers who supplemented a low-calorie diet with casein lost more fat and gained more strength than police officers who supplemented a low-calorie diet with whey protein. (3) But since then, a bulk of research has concluded that there is no practical difference in the muscle-building activity between whey and casein protein. (4)(5)(6)
What research has told us is that both whey and casein may have superior effects compared to certain vegan protein powders, (7)(12) though that notion has also been challenged by more recent research. (8)(9)One thing worth considering is that casein digests more slowly than whey, so some find it to be a little more filling, though research isn’t unanimous. (10)(11)(12) While both whey and casein are great ways to manage appetite, if hunger is a big obstacle for you, then casein could potentially be a better pick. Also, you may be able to find a whey casein blend to get the best of both worlds.
[Related: IIFYM (If It Fits Your Macros): Your Ultimate Guide To This Diet]
Casein Protein Powder FAQs
Is casein or whey better for weight loss?
Neither one of these milk proteins are superior for weight loss. Neither protein is more anabolic or “fat burning.” However, casein does digest more slowly so some find it a more filling snack. If it helps you eat less, it’s a good supplement for weight loss.
Does casein protein powder contain lactose?
It has very little lactose, less than whey protein, however it’s not always lactose-free. If there’s no sugar on the label then there’s under half a gram of lactose per serving, and probably none. But people with serious allergies should contact the manufacturer to confirm.
Should I have casein protein before bed?
Casein is a slow-digesting protein, so it will release amino acids into your bloodstream for a longer period of time than a lot of other proteins, like whey. The slower digestion rate can make it more filling and might prevent midnight snacking, but it doesn’t make it more “anabolic” than other protein.
How much do casein protein powders cost?
Casein is on par price-wise to whey protein. All of our top picks fall between about $1.00 to $2.00 per serving with an average of around $1.61. Depending on quality, ingredients, and options to buy in bulk, you will see the price fluctuate.
What is the best casein protein?
After doing a deep dive into all of the top-tier choices this list of casein has to offer, we decided that Transparent Labs Casein is our top choice. The formula is all-natural and derived from 100 percent grass-fed cows. Not to mention, it provides 25 grams of protein per serving. It comes in chocolate or vanilla flavors and is sweetened with stevia.
References
- Abbott, W., Brett, A., Cockburn, E., & Clifford, T. (n.d. ). Presleep Casein Protein Ingestion: Acceleration of Functional Recovery in Professional Soccer Players. International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 14(3), 385-391. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijspp.2018-0385
- Kim J. Pre-sleep casein protein ingestion: new paradigm in post-exercise recovery nutrition. Phys Act Nutr. 2020;24(2):6-10. https://doi:10.20463/pan.2020.0009
- Demling RH, DeSanti L. Effect of a hypocaloric diet, increased protein intake and resistance training on lean mass gains and fat mass loss in overweight police officers. Ann Nutr Metab. 2000;44(1):21-29. https://doi:10.1159/000012817
- Trommelen, J., van Lieshout, G.A.A., Pabla, P. et al. Pre-sleep Protein Ingestion Increases Mitochondrial Protein Synthesis Rates During Overnight Recovery from Endurance Exercise: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sports Med 53, 1445–1455 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-023-01822-3
- Wilborn CD, Taylor LW, Outlaw J, et al. The Effects of Pre- and Post-Exercise Whey vs. Casein Protein Consumption on Body Composition and Performance Measures in Collegiate Female Athletes. J Sports Sci Med. 2013;12(1):74-79. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24149728/
- Fabre M, Hausswirth C, Tiollier E, et al. Effects of Postexercise Protein Intake on Muscle Mass and Strength During Resistance Training: Is There an Optimal Ratio Between Fast and Slow Proteins?. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2017;27(5):448-457. https://doi:10.1123/ijsnem.2016-0333
- Kanda A, Nakayama K, Sanbongi C, Nagata M, Ikegami S, Itoh H. Effects of Whey, Caseinate, or Milk Protein Ingestion on Muscle Protein Synthesis after Exercise. Nutrients. 2016;8(6):339. Published 2016 Jun 3. https://doi:10.3390/nu8060339
- Banaszek A, Townsend JR, Bender D, Vantrease WC, Marshall AC, Johnson KD. The Effects of Whey vs. Pea Protein on Physical Adaptations Following 8-Weeks of High-Intensity Functional Training (HIFT): A Pilot Study. Sports (Basel). 2019;7(1):12. Published 2019 Jan 4. https://doi:10.3390/sports7010012
- Messina M, Lynch H, Dickinson JM, Reed KE. No Difference Between the Effects of Supplementing With Soy Protein Versus Animal Protein on Gains in Muscle Mass and Strength in Response to Resistance Exercise. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2018;28(6):674-685. https://doi:10.1123/ijsnem.2018-0071
- Abou-Samra, R., Keersmaekers, L., Brienza, D., Mukherjee, R., & Macé, K. (2011). Effect of different protein sources on satiation and short-term satiety when consumed as a starter. Nutrition journal, 10, 139. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-10-139
- Dhillon, J., Craig, B. A., Leidy, H. J., Amankwaah, A. F., Osei-Boadi Anguah, K., Jacobs, A., Jones, B. L., Jones, J. B., Keeler, C. L., Keller, C. E., McCrory, M. A., Rivera, R. L., Slebodnik, M., Mattes, R. D., & Tucker, R. M. (2016). The Effects of Increased Protein Intake on Fullness: A Meta-Analysis and Its Limitations. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 116(6), 968–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2016.01.003
- Bendtsen LQ, Lorenzen JK, Bendsen NT, Rasmussen C, Astrup A. Effect of dairy proteins on appetite, energy expenditure, body weight, and composition: a review of the evidence from controlled clinical trials. Adv Nutr. 2013;4(4):418-438. Published 2013 Jul 1. https://doi:10.3945/an.113.003723
- Del Pozo, S., Gómez-Martínez, S., Díaz, L. E., Nova, E., Urrialde, R., & Marcos, A. (2022). Potential Effects of Sucralose and Saccharin on Gut Microbiota: A Review. Nutrients, 14(8), 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081682
- Hernández-Camacho, J. D., Vicente-García, C., Parsons, D. S., & Navas-Enamorado, I. (2020). Zinc at the crossroads of exercise and proteostasis. Redox biology, 35, 101529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101529
- Carbone, J. W., & Pasiakos, S. M. (2019). Dietary Protein and Muscle Mass: Translating Science to Application and Health Benefit. Nutrients, 11(5), 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051136
- Church, D. D., Hirsch, K. R., Park, S., Kim, I. Y., Gwin, J. A., Pasiakos, S. M., Wolfe, R. R., & Ferrando, A. A. (2020). Essential Amino Acids and Protein Synthesis: Insights into Maximizing the Muscle and Whole-Body Response to Feeding. Nutrients, 12(12), 3717. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123717
- Kong, W., Xie, Y., Hu, J., Ding, W., & Cao, C. (2024). Higher ultra processed foods intake is associated with low muscle mass in young to middle-aged adults: a cross-sectional NHANES study. Frontiers in nutrition, 11, 1280665. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2024.1280665